Anthropic's Blueprint for Building Effective AI Agent Systems
How to Turn Your Business Processes Into AI Workflows (4 Proven Patterns)
In our recent posts, we've explored how AI agents are reshaping business operations and where the technology is finally ready for real work. Now comes the question everyone's been asking: "How do I actually build one?"
Most businesses hear "AI agents" and imagine some complex, autonomous system that requires a PhD to understand. The reality is much simpler.
Research from Anthropic, based on analyzing dozens of successful AI implementations across industries, reveals that the most effective AI Agent systems follow surprisingly simple patterns.
Let's explore the two building blocks required to get started: (1) the augmented LLM and (2) four proven workflow patterns.
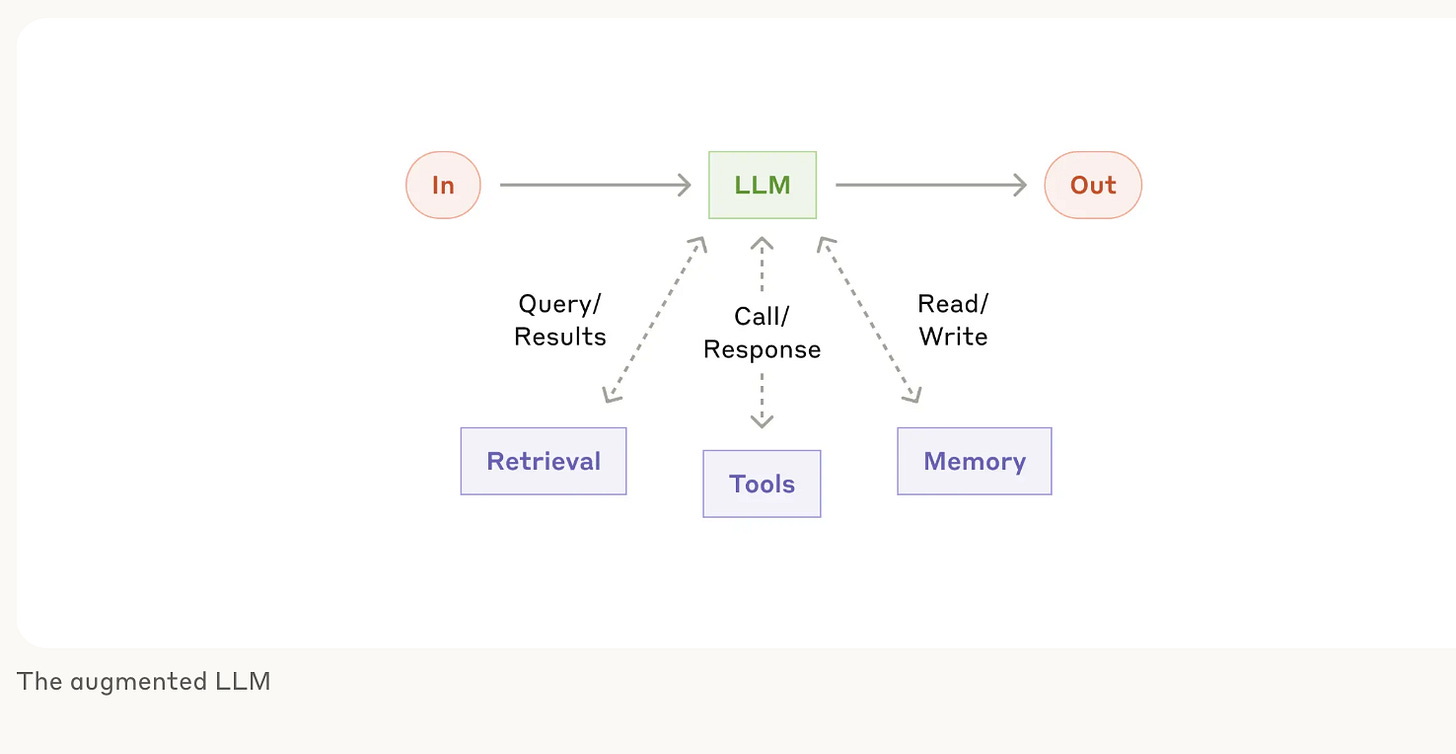
The Augmented LLM
Before we dive into the four workflow patterns, let’s discuss what makes an AI agent different from regular ChatGPT.
AI agent systems are AI applications that can take actions, use tools, and work through multi-step processes rather than just answering questions. Instead of a simple back-and-forth chat, these systems can actually do things: search databases, send emails, analyze data, or update your CRM systems.
Successful AI agent system starts with an "augmented LLM” - a regular AI model enhanced with three key capabilities:
Retrieval: can search and find information from databases, documents, or the internet
Tools: Can take actions like sending emails, making calculations, or updating systems
Memory: Can remember important information from previous interactions
Think of it like ChatGPT with hands, eyes, and a notebook.
The good news is that you don't have to build these connections from scratch. Anthropic's Model Context Protocol (MCP) makes connecting to tools easy by allowing developers to plug into a growing ecosystem of third-party capabilities.
Four Workflow Patterns to Get Started
Having an augmented LLM isn't enough. The next step is to define your workflow—structured paths that tells your AI how to handle complex tasks. Think of these as the step-by-step processes you'd give to a human employee, but designed for AI to follow.
Here are four proven patterns to follow:
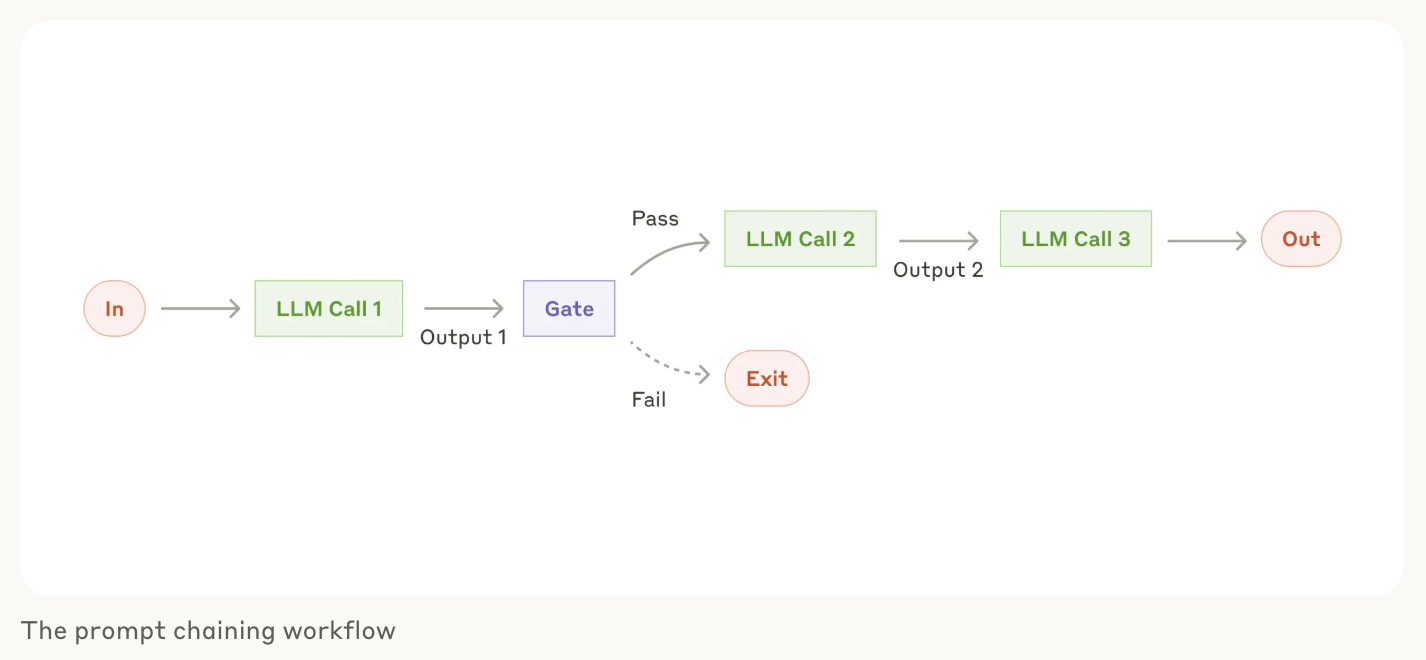
Workflow Pattern 1: Prompt chaining (The Assembly Line)
What it does: Breaks complex tasks into sequential steps, where each LLM call handles one piece and passes results to the next. You can add human checks (i.e. "gate” in the diagram below) on any intermediate steps to ensure that the process is still on track.
Best for: Tasks you can break into clear, predictable steps
Example: Writing an outline of a document, checking that the outline meets certain criteria, then writing the document based on the outline.
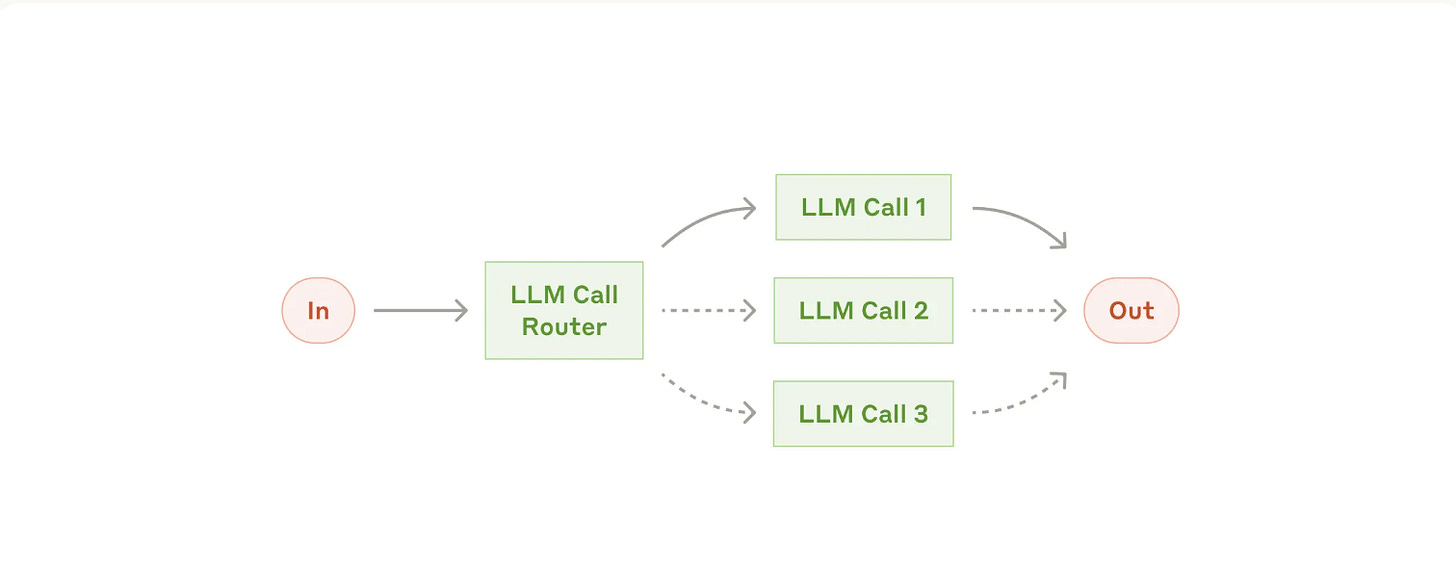
Workflow Pattern 2: Routing (The Smart Dispatcher)
What it does: Analyzes incoming requests and automatically routes them to the right specialized process.
Best for: Situations where different types of inputs need different handling
Example: Directing different types of customer service queries (general questions, refund requests, technical support) into different downstream processes, prompts, and tools.
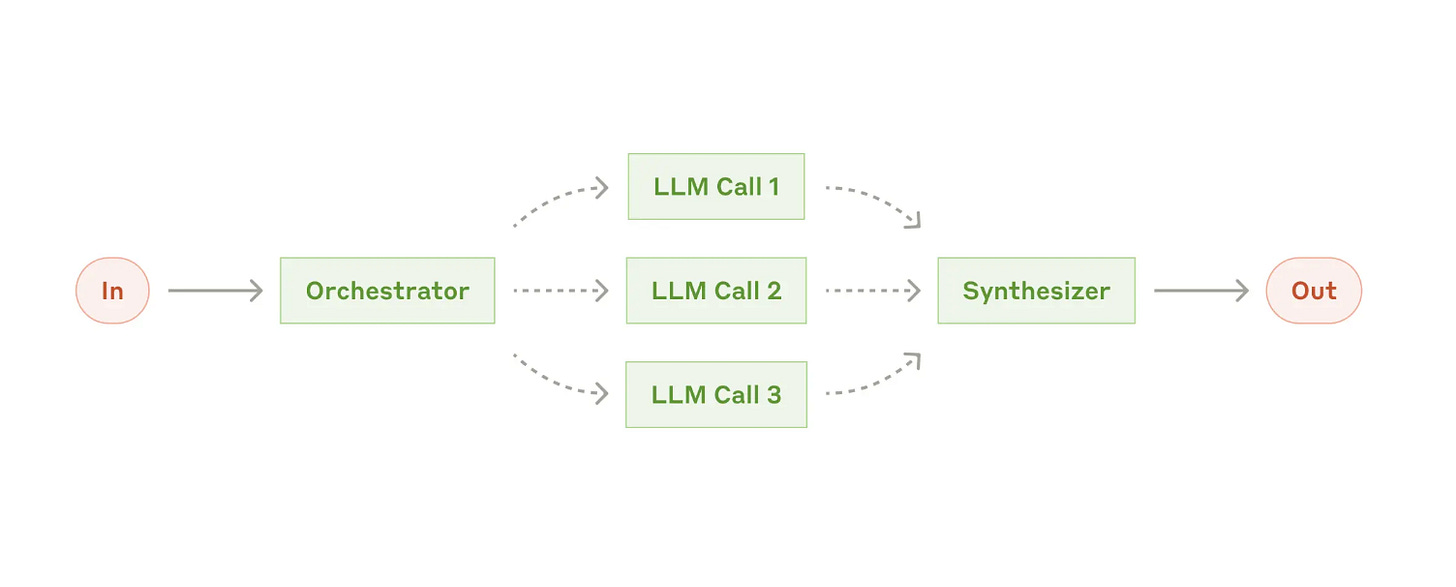
Workflow Pattern 3: Orchestrator-workers (The Dynamic Project Manager)
What it does: Like a project manager, a central LLM analyzes complex tasks, breaks them down and assigns pieces to specialized workers, then combines the results.
Best for: Complex tasks where you can't predict all the steps beforehand
Example: Search tasks that involve gathering and analyzing information from multiple sources for possible relevant information.
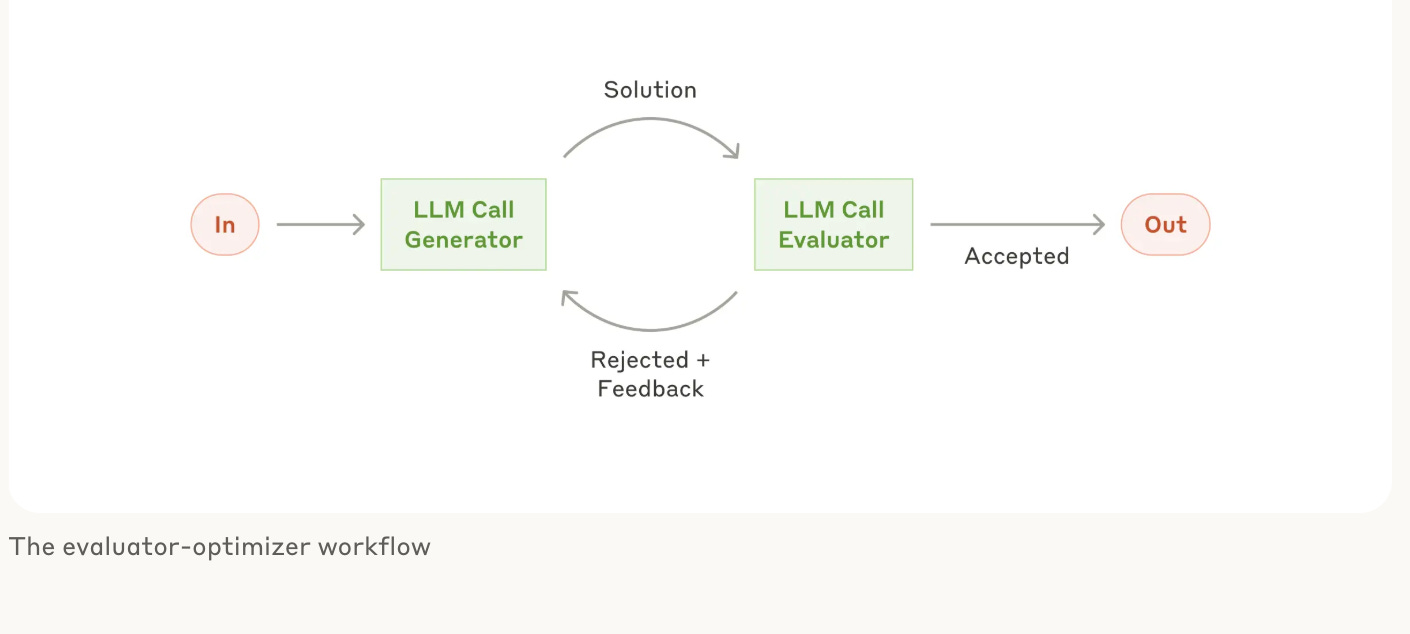
Workflow Pattern 4: Evaluator-optimizer (The Quality Control)
What it does: Like having a built-in editor, one LLM generates a response while another evaluates and provides feedback in a continuous improvement loop.
Best for: Tasks where iterative refinement adds clear value and you have clear evaluation criteria
Example: Literary translation where there are nuances that the translator LLM might not capture initially, but where an evaluator LLM can provide useful critiques.
From Patterns to Practice: A Simple Decision Framework
Now that we understand the four workflow patterns, the question becomes: how do you actually choose and implement the right one for your business?
Look at a process in your business that involves multiple steps or decisions. Ask yourself:
Can this be broken into clear sequential steps? Start with Prompt Chaining
Do different inputs need different handling? Try Routing
Is this too complex to predict all steps? Use Orchestrator-Workers
Does the output need iterative improvement? Build Evaluator-Optimizer
Your Next Move: This week, pick one repetitive process in your business and map it to these four patterns—the technology is ready, so which problem will you solve first?


Hey, I came across your newsletter and just wanted to say it really caught my eye. Thought I’d take a moment to drop by and share a bit of support. If you ever feel like exchanging thoughts in my newsletter, I would really welcome that.